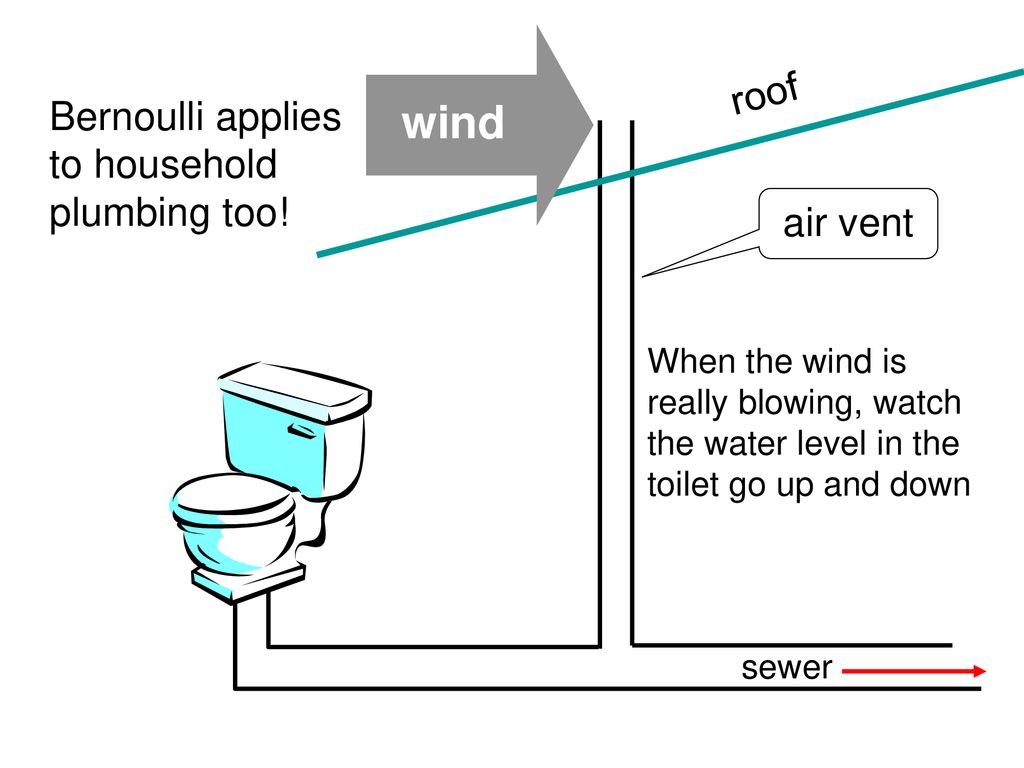
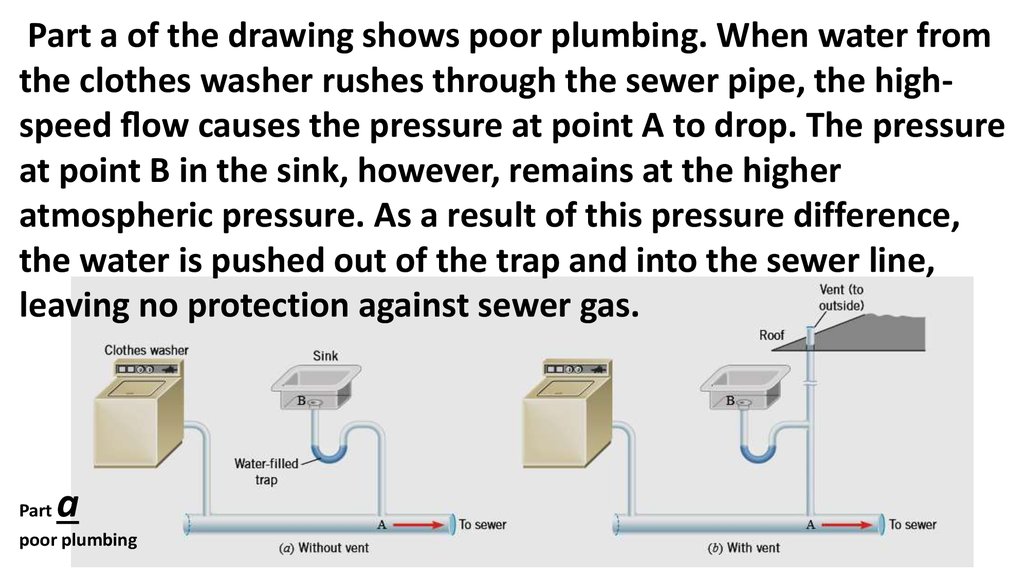
Roof Pushed Up Or Down Bernoulli
This allows some slack in the roof.
Roof pushed up or down bernoulli. What seems to happen is that the wind against the front of the trailer pushes the front of the trailer back flex in the structure. This is solved using bernoulli s equation and the definition of pressure. Endgroup peter shor dec 9. The roof is flat so the air pushing up from the inside is at the same depth as the air pushing down on the outside so tex y 1 y 2 tex.
If it is reduced further the flow boundary will at first be sucked down and will continue to flow along the slope and a. So i can rearrange bernoulli s equation. Airplanes fly upside down etc. According to bernoulli the faster flow over the top corresponds to a lower pressure and provides lift to the wing.
They are sucked off as the high winds passing over the roof tops lowers the pressure iaw bernoulli s principle. This causes the streamlined flow to be pushed up even further so that pressure occurs on the windward slope. Bernoulli s principle still holds. Thus the pressure inside the building is higher than on the outside.
You can t really see an issue when the trailer is parked. This concept can be derived from newton s 2nd law of motion. Approximately what is the force due to the bernoulli effect on a roof having an area of 220 m 2. What happens is the roof is pushed inward and collapses the wind inside the house blows out the roof from the inside the higher pressure inside lifts the roof off the walls friction rips up the roof and blows it apart.
Storm winds blowing at high speed over a roof can destroy the roof of a closed up house because of bernoulli s principle. I doubt it s a leak but who knows. Air flows faster over the top of an airfoil than under the bottom thereby making bernoulli s principle relevant figure 3. The classic example of bernoulli s principle involves airflow over airplane wings.
When a strong wind kicks up the pressure outside drops but there isn t time for air to flow in and out of the house to cause the corresponding drop in the interior pressure. The physics of roof ventilation the bernoulli effect. This then allows it to balloon up. Since the air is still inside.
Bernoulli s principle as stated in the text assumes laminar flow. Tex p 2 p 1 frac 1 2 rho v 1 2 tex i think that the net force should be. This will allow us to eliminate many of the terms. If the slope of the roof is reduced a point will be reached at which pressure on the windward slope becomes zero.
Typical air density in boulder is 1 14 kg m 3 and the corresponding atmospheric pressure is 8 89 10 4 n m 2. And the net force is upward and outward something like how an airplane wing works as the airspeed over the top of the wing is faster than below it. That s why you get a pressure gradient across the roof. It is a system of intake and exhaust.
I m also assuming that the velocity of the air inside the house is zero tex v 2 0 tex. First choose the bernoulli points one just inside the roof where the air is still point a and one just outside where the air is moving point b.